Risk Governance Framework and Capital Management Framework
The Group's Risk Governance Framework (RGF) and Capital Management Framework rest on five pillars: a) effective Board oversight, b) sound risk management strategy, c) dynamic capital management process, d) risk and capital monitoring and escalation, and e) review and validation. The Group's risk management strategy and capital management systems respond to internal and external signals. Internal signals are manifested in its corporate Mission & Vision, which animate a set of strategies that aim to fulfill such vision while taking into account external indicators mostly involving current market movements and projections. Always, the RGF and Capital Management Framework see through bi-focal lenses - growth/business-as-usual scenario, and stress. With the foregoing as backdrop, business targets are determined along with the risks and the necessary capital, bearing in mind minimum capital adequacy regulations and internal triggers. In an ideal scenario, the process should lead to maximization of capital via robust capital allocation among the business units, and with performance assessed via risk-adjusted measures. The Group is committed to working towards this goal. The Frameworks and corresponding sub-processes are all subject to review and validation, a role largely driven by the Internal Audit Group. Finally, each facet of the Frameworks is monitored and reported to the designated oversight bodies.
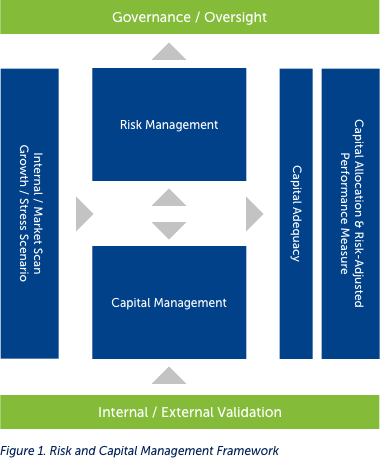
Risk Governance Framework
The Risk Governance Framework of the Group follows a top-down approach, whereby the Board of Directors (Board) takes ultimate accountability for: the risks taken, setting the tolerance level for these risks, business strategies, operating budget, policies, and overall risk philosophy.
In the interest of promoting efficient corporate governance, the Board constitutes committees to perform oversight responsibilities. These committees perform oversight functions in the area of risk policy formulation, decision-making, and risk portfolio management.

Board of Directors
The Board ensures that the Group‘s corporate objectives are supported by a sound risk strategy and an effective risk governance framework that is appropriate to the nature, scale, and complexity of its activities. The Board provides effective oversight of senior management‘s actions to ensure consistency with the risk strategy and policies, including the risk appetite framework. The Board:
- Sets policies, strategies and objectives and oversees the executive function
- Sets the risk appetite and ensures that it is reflected in the business strategy and cascaded throughout the organization
- Establishes and oversees an effective risk governance and organizational structure
The Risk Oversight Committee
The ROC supports the Board with respect to oversight and management of risk exposures of the RCBC parent bank and subsidiaries (the Group). In this regard, the ROC exercises authority over all other risk committees of the Group, with the principal purpose of assisting the Board in fulfilling its risk oversight responsibilities. The ROC oversees:
- The risk governance framework
- Adherence to risk appetite
- The risk management function
- Capital planning and management
- Recovery plans
The Risk Management Groups
Supporting the ROC in carrying out its mandate are the Risk Management Group (RMG), and the Credit Management Group (CMG), headed by the Chief Risk Officer (CRO) and the Chief Credit Officer, respectively.
Administratively and functionally, enterprise risk management follows the - "centralized risk monitoring – decentralized risk management" approach. The risk units in the subsidiaries implement the risk management process individually, and report to their respective risk committees.
The Parent Bank‘s risk management groups implement the risk management process in the parent and consolidate the risk MIS from the various subsidiary risk units for a unified risk profile that is presented to the ROC.
The risk management groups are responsible for overseeing the risk-taking activities across the Group, as well as in evaluating whether these remain consistent with the Bank‘s risk appetite and strategic direction. It shall ensure that the Risk Governance Framework remains appropriate relative to the complexity of the Bank‘s risk-taking activities. The risk management groups shall be responsible for identifying, measuring, monitoring, and reporting risk on an enterprise-wide basis. It shall directly report to the ROC. Personnel in the risk management groups should collectively have knowledge and technical skills commensurate with the Bank‘s business activities and risk exposures.
The Risk Management Group (RMG)

The following are the major risk management divisions and departments under RMG:

Sustainable Finance Division: The Chief Sustainability Officer (CSO) is tasked to lead and oversee the Bank’s sustainability efforts and harmonize such with different groups and subsidiaries of the Bank. The CSO also serves as the Head of Sustainable Finance Division (SFD) which primarily handles credit risk mitigation, capital adequacy measurement, regulatory compliance, and E&S risk mitigation functions. Credit risk mitigation falls under Independent Credit Review which was created in line with the requirements of BSP Circular 855 on credit review process. This is complemented by activities involving measurement and monitoring of BSP requirements on lending, capital adequacy,
back testing, model performance review, and stress testing, all of which are handled by the Portfolio Analytics Department.
E&S risk mitigation is handled by the Sustainable Asset Management and Sustainable Lending Departments which are tasked to implement RCBC’s Sustainable Finance Framework and Environmental and Social Management System (ESMS) Policy, respectively. This is in support of MORB Section 153 and of the Bank’s commitment to uphold E&S responsibility in all its
business activities. Regular SFD updates are submitted to the ROC. SFD contributes to risk portfolio management and attainment of financial sustainability through the assessment of the Bank’s overall portfolio quality in terms of credit risk, capital adequacy, regulatory compliance, and E&S impact.
Market and Liquidity Risk Management Division: The Market and Liquidity Risk Management Division (MLRMD) is primarily tasked with the development and implementation of market risk, liquidity risk, and interest rate risk in the banking book (IRRBB) policies and measurement methodologies, recommending and monitoring compliance to risk limits, and reporting the same to the appropriate bodies. It regularly reports to the ROC and the Asset & Liability Committee (ALCO) activities relevant to market risk, liquidity risk, and IRRBB management of the Group.

Operational Risk Management Department; The Operational Risk Management Division (ORMD) was created to ensure that operational risks are managed at an enterprise level, the systems and processes used to manage these risks are effectively implemented, and that management of these risks is embedded in the Group’s processes.
ORMD is tasked to ensure implementation of the Operational Risk Management Framework (ORMF) across the Group; and to develop an appropriate operational risk management environment where operational risks are identified, assessed, reported, monitored, and controlled/mitigated. It is also expected to identify and recommend mitigants for emerging risk types, and to promote and maintain quality operational risk programs and infrastructure. ORMD also ensures the timely and quality renewal of institutional-wide insurance policies to protect the Bank against unexpected
and substantial unforeseeable losses.
ORMD, through the Business Resiliency Department (BRD) is responsible for ensuring the Bank’s capability to plan and respond to incidents and business disruptions and enable the continuity of key business operations at predefined acceptable levels.
ORMD, through the Reputational Risk Department (RRD), provides the processes and methodologies designed to protect the clients via the Bank’s Financial Consumer Protection Assistance Mechanism (FCPAM), Consumer Protection Framework and Reputational Risk Framework.
To facilitate implementation of ORM tools in the various business lines of both the parent bank and its subsidiaries, various officers are deputized and serve as embedded Deputy Operational Risk Officers (DORO), Consumer Assistance Officers (CAO) and Business Continuity Planning (BCP) Leaders. A DORO, CAO or BCP Leader functions as ORMD’s liaison to and implementation
arm in the various business units for Operational Risk, Reputational Risk and Business Resiliency, respectively.

Enterprise Fraud Risk Department: The Enterprise Fraud Risk Department (EFRD) is tasked to ensure proper observance of the fraud management program (i.e., prevention, detection, investigation and escalation, containment and recovery, analysis and recommendation), and provide a high-level Enterprise-wide Fraud Risk Management Framework and its corresponding policies and standards. This serves as the basis upon which the Business, Operations and Support units will develop their own specific procedures and guidelines that will operationalize the controls to mitigate fraud risks that are inherent in their day-to-day activities. EFRD also conducts periodic analysis of all fraud incidents and losses, creates rules/parameters for monitoring, investigates fraud cases, and determines current and emerging fraud risk trends which are reported to the BOD, through the ROC, and to the Management, thereby assisting them to make
well-informed fraud risk management decisions.

Information Security Governance Department: The Information Security Governance Department (ISGD) deals with all aspects of information whether spoken, written, printed, electronic, or relegated to any other medium regardless of whether it is being created, viewed, transported, stored, or destroyed. This covers all business units, branches/offices, and subsidiaries, both domestic and overseas, third party institutions, and individuals.
The ISGD is tasked to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements set forth by the regulating bodies and laws in the areas of information security and electronic banking services. The department monitors and ensures that policies, procedures, and standards in managing information security and technology risk are observed across the Group. It also oversees and is part of the process for detecting, analyzing, and responding to any information security incident. ISGD also keeps the Board and senior management apprised on information security risks.
ISGD executes an Information Security Strategic Plan (ISSP) and Information Security Program (ISPr) aligned with the business objectives of the Group. The department also establishes governance-specific policies, standards, and procedures for information security risk management, conducts trainings and issues advisories to increase information security awareness, and performs the Information Security Risk Assessment (ISRA) and Information Security Annual Certification (ISAC) for the whole RCBC Group to manage, identify, and address information security risks.
The Credit Management Group (CMG)
The Credit Management Group (CMG) focuses on the operational and front-end aspect of the credit cycle.

Major responsibilities of CMG include:
As the 2nd line of defense, CMG achieves its mandate through:
1. Setting up of credit policies and guidelines that standardize lending principles across units (consumer and business lending)
2. Involvement of credit analysts in area of lending that cannot be automated via straight through processing (STP)
a. Consumer Loans. Credit analysts continue to be involved in the execution of required policy and procedures defined for credit checks done on each customer. This will eventually evolve into
exception handling for accounts that cannot be processed via STP.
b. Business Loans. Credit analysts corroborate with relationship managers (RMs) in setting-up credit proposals for customers, ensuring all aspects of credit as required by policy are included. CMG is expected to articulate unresolved issues (with the RM) that final approvers can decide on.
3. Providing reasonable assurance to stakeholders on the quality of the Bank’s loan books through:
a. Monitoring and reporting of the Bank’s asset quality with adoption of an early warning framework
b. Calibration of existing policies, guidelines and procedures as necessary
c. Supporting the RMs in developing strategies to effectively minimize delinquency flows
4. Ensuring that the Bank is adequately provisioned across its lending portfolio.
Capital Management Framework
The Capital Management Framework of the Group incorporates the planning process, the Capital Plan, and the continuing review and reporting of results.
Strategic and Business Planning
In the Strategic and Business Planning Process of the UniBank, the overall risk appetite is developed as part of the business plans.
The process involves the development of strategic and business objectives, anchored on the Mission & Vision, as interpreted and articulated by Senior Management. This is an iterative process involving both internal and external analyses and risk assessment.
The planning process then results in a business plan, the annual budget, medium-term forecast/projections, which all incorporate identified risks. It includes a regular review of the business plan (monthly, quarterly) based on key performance indicators.
Capital Planning
The other component of the Framework is the development of the Capital Plan that incorporates the current business plan and additional projections and stress testing.
This component highlights the use of medium to long-term forecasts and stress scenarios in the management of capital. The results of the forecasts are always reviewed against the internal minimum capital ratios, inclusive of Pillar 2 charges, and the regulatory minimum.
More details on the Group’s RGF and Capital Management Framework can be found in the published Annual and Sustainability Report (https://www.rcbc.com/annual-reports).

















